

 [羅戈導讀]此篇文章接上篇CSCP-Module 1: Supply Chain Design。
[羅戈導讀]此篇文章接上篇CSCP-Module 1: Supply Chain Design。

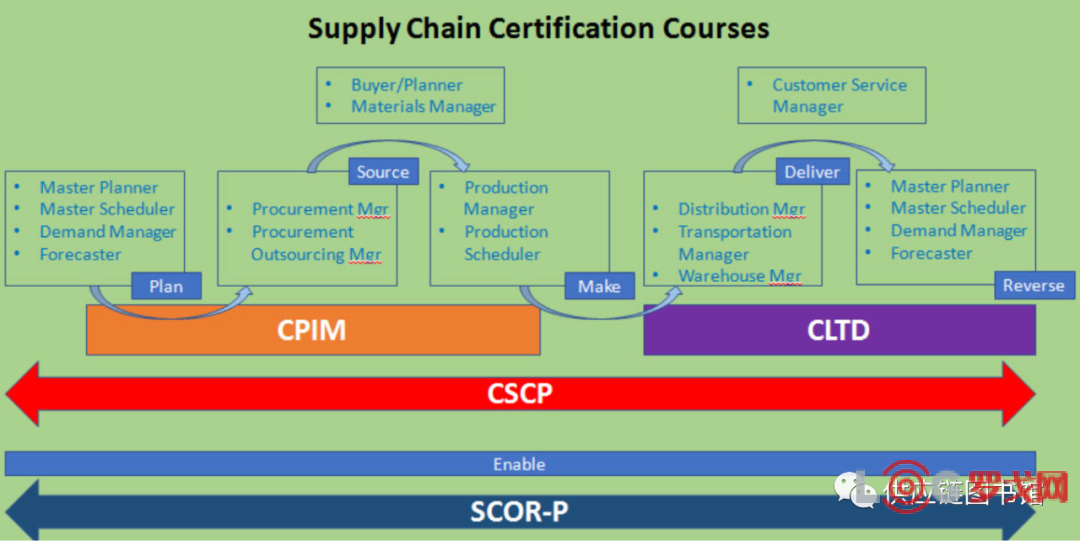
此篇文章接上篇CSCP-Module 1: Supply Chain Design。
因教材本身目前是英文版,筆記同為英文版,偶爾穿插中文注釋,及相對原教材的摘取刪減。
Module 2: Supply Chain Planning & Execution
Chapter 1: components of DM(Demand Management)
1) DM is the art of synchronizing supply and demand plans
Long-term demand--->long term forecasting, product development, capacity development
Mid-term demand--->S &OP
Short-term demand--->item level master scheduling
2) DM Process: balance demand & firm's output capabilities
Planning demand
Communicating demand
Influencing demand
Prioritizing demand
Topic1: Planning demand(18 months)
1) Demand plan inputs:
Forecast/product & brand management/marketing/sales/business plan & strategy/assumptions used & level of uncertainty(assumptions should be documented, reviewed, challenged in monthly SOP)
用處:
Demand in units/dollars
Validation &control of plans of individual departments
Topic2: Communicating demand
1) Structure communication:
An output of SOP process: the supply side uses the consensus numbers to perform master scheduling and supply planning
Demand manager:
An intermediary between supply and demand
Communicate organization's supply and demand synchronization efforts
Topic3: Influencing demand
PDCA: involve product & brand management, marketing, sales activities
Topic4: DM functional responsibilities /interfaces
Product development & brand management: long term
Marketing: interface with DM in mid and short term
Sales: implement demand plan commitments regarding influencing or prioritizing demand
Operations
Topic5: Link DM Components
CPFR:
Develop effective business process to synchronize SC operations across enterprise boundaries
Challenges: increased cost, resistance to infor/data sharing, bridging internal functions
DI: Distribution integration
Quick-response programs(QRP)
Imploy POS, EDI, may direct shipment from a factory to a retailer
Can receive significant reductions in lead times
Continuous replenishment(CR)--> Goal: lower associated cost, high inventory turnover
Rely on sharing of POS data by retailer and supplier
Supplier notified daily of actual sales/warehouse shipments and commitment to replenishment
VMI
Vendor: with access to customer's POS inventory data
Consignment:= vendor-owned inventory(VOI)
Goal of VMI: the supplier to control ordering process
VMI Measurements: bullwhip effect/inventory cost/stock-out/lead time 降低;on-time delivery/inventory turn升高
Chapter 2: Forecasting demand
Forecast process
Chapter3: Demand prioritization
Topic1: demand prioritization policies and processes
1) Demand prioritization:
Setting time fences
Allocation of supply
Need a clear prioritization policy and implement it using a structured process
DM and prioritization policy
Measures of customer service levels
Represents SC's Roles in fulfilling marketing objectives
Measures of basic customer service are fill rates, lead time, order status, monitoring, customer satisfication
Topic2: Time fences(Decision points)
Topic3: Allocation of supply
Commitment decision point
Chapter4: Operations planning and control
Topic1:Strategic business master resource planning
Demandplan/Long-term fcst--input-->business plan--output-->budgets/projectedfinancial statements
Topic2: S&OP
1) S&OP Process
Review performance(product review meeting)
Provide demand-side professionals with vital infor. On which to base their assumptions
Evaluating demand levels(demand planning)
Review at product family level
Close the gap between demand plan and business plan revenue goals
產生一個Updated medium-term demand plan (use as a basis for supply planning phase & financial reviews)
Evaluating supply capability(supply planning)
Reconciling demand, supply, financial plans
2) Implementing S&OP
Getting buy-in on SOP's coordinating functions: communication, one plan to unite all major functions, sales, operation finance
Emphasizing each party's contributions to SOP
Product, brand management, marketing, sales contributions
Operations contributions
Operations strategies:(eg. Level production strategy, chase production method, hybrid strategy)
Supply-demand strategies:MTS(mass market strategy)/MTO/ETO/ATO
Building enthusiasm for SOP among SC managers
3) S&OP Benefits
Link between business planning & tactics
Opportunities to be proactive rather than reactive
Definitive short-to-medium-term plan
Unified, cross-functional plan and processes
Bridge between customer value & supply chain efficiency
Incentive to engage in continuous improvement
S&OP會產生一個production plan based on product family level
Chapter 5: Master scheduling
Topic2: Materials & Inventory: (MRP & DRP)
Offsetting: process of counting backward from a due date to accommodate lead time
Pegging: as active where-used infor
Reconciling JIT/Lean with MRP: small bucket or bucket less system/ balanced flow
DRP
定義:the function of determining the need to replenish inventory at branch warehouses(即distribution centers)
Logic: translate DC demand into forecasts for use in factory master scheduling
Push system & pull system & hybrid system
Chapter6: Capacity management, planning and control
1) Resource planning: identify the number of labor hours required quarterly to meet operation goals (product family level)
Resource profile
Staging capacity investments: one-step lead strategy/stepwise lead strategy/stepwise overlapping strategy
2) RCCP
Review key resources and bottleneck areas(individual items level)
Typically check bottlenecks, gateway work centers, critical suppliers
3) CRP
4) PAC
5) Measuring capacity
Rated capacity= available time * utilization * efficiency
Demonstrated capacity= output for n periods/n
Demand pull: the triggering of material movement to a work center only when that work center is ready to begin next job.
Kanban: idea is to keep lot sizes as small as possible to optimize use of space and labor
Chapter7: Inventory
Topic1: Inventory Basis
1) Types of inventory
Raw material inventory
WIP inventory
FG inventory
MRO(Maintenance/Repair/Operating Suppliers) inventory
In-transit(distribution or pipeline) inventory (measured by average annual inventory in-transit, to reduce transit time)
2) Functions of Inventory
Anticipation inventory
Safety inventory(fluctuation inventory)
Lot-size inventory or cycle stock ( for discounts)
Hedge inventory (為了外界風險囤積庫存)
Buffer inventory (和約束理論TOL有關)
Decoupling (allow supply & demand functions to operate at differing ,independent rates)
3) Inventory management (plan & control inventory)
KPI
reduction of inventory costs related to holding, ordering, transporting at various points of SC;
Achievement of customer service targets related to quality, availability, on-time delivery of products and services
Inventory policy
定義: a way of formlizing results of strategic inventory decisions
Broad inventory management decisions: eg. Specify centralized or decentralized inventory planning /warehousing; frequency of communications; positioning strategy such as postponement
Specific level inventory management decisions
Specify rules for order qty. timing
Amounts of specific items to purchase vs produce
Factors when setting inventory policy
Customer demand
Planning horizon
Replenishment lead time
Product variability
Inventory costs
Customer service requirements
Topic2: Aggregate & Item inventorymanagement總體庫存管理
1) Concerned with financial impact of inventories
2) ABC法:
Based on monetary value of inventory
ERP usually segregate ABC systems for the purpose of counting
Using ABC as a policy may require using a different identification data field
3) Item inventory management
Goal: to enable planners to translate strategic inventory goals into measurable results
Implemented through inventory planning, control
Topic3: Inventory costs and accounting
1) Acquisition cost 購置成本(purchase price)
2) Landed cost
Purchased inventory: sum of all direct costs(price, transportation, customs, insurance)
Internally sourced inventory: factory overhead costs, direct labor, direct materials
3) Carrying cost(holding cost) (15%-40%)
Include all expenses involved in housing the inventory
Storage costs
Capital costs
Risk costs
4) Ordering cost
Effects of inventory on financial statements(balance sheet/income statement/statement of cash flows)
Chapter 8: Inventory planning
Topic1: Inventory planning basics
1) Two major components
Where to locate inventory
Desired level of items at each selected locations
2) 備注:概念break-bulking散貨warehouses
Topic2: Inventory control
1) Determine two things
How much to order
When(how often) to order
2) important considerations
Determine order qty. (lot-for-lot/fixed order qty/EOQ)
Determine ordering systems(inventory ordering system as inventory models for replenishment of inventory)
Ordering point system(fixed amount)
Periodic review system(fixed time)
Min-max system
Time-phased order point system
Safety stock, safety lead time
3) Assessing inventory accuracy (inventory adjustment)--->two approaches to keep accurate inventory
Periodic counting
Cycle counting: purpose to identify items in error
Chapter 9: Supply Management
Topic1: Total cost of ownership (TCO)
Tangible costs: Can be given a value using objective measures
Intangible costs: eg.Customer satisfaction, employee morale, quality, risk, etc.
Landed cost
Process change cost
Ongoing cost
Net cost
Topic2: Make-versus-Buy analysis
1) Choose activities to contract out
Core competency?
The consequence of losing related skills/knowledge
What's the landed cost or total cost of ownership
2) 概念:
offshoring: outsource a business functions to another company in a different country than the original company's country
Reason for offshoring: needs for specific country/ market growth
Topic3: range of buyer-supplier relationships
(proximity---visibility---integrationwith competitors---communication---culture)
Buy on the market
Ongoing relationship
Partnership
Collaboration/strategic alliance--> blanket purchase order: long term commitment to suppliers
Merger/acquisition
Topic4: developing supply plans
(thestrategic design of a supply network based on total cost of ownership)
Make-versus-buydecisions, desired level of buyer-supplier relationship
1)Plan validation and replenishment
Corporate strategy alignment
Supply planning process input: corporate strategy
Meeting corporate goals for customer service, production capacity, quality
Corporate mission and culture alignment
Risk assessment
Centralized versus autonomous sourcing
(balance: centralized control for strategic sourcing with someautonomy for non-strategic sourcing )
2)Plan finalization
One way that supply plans can be refined and implemented is by using supplier relationship management
后續模塊將持續更新,敬請關注與期待。

中郵無人機(北京)有限公司揭牌
2146 閱讀
智能倉儲企業“智世機器人”完成數千萬元A輪融資
1557 閱讀
聊聊2025年物流企業如何做營銷規劃
1527 閱讀這家老牌物流巨頭被整合重組,四千多名員工將何去何從?
1431 閱讀物流供應鏈領域“吸金”不力,但能給投融資事件頒幾個獎
937 閱讀極兔速遞2024年第四季度包裹量增長32.5% 全球日均單量超8000萬件
951 閱讀京東緊急馳援西藏震區,首批救援物資已由專車送出
941 閱讀2024LOG供應鏈物流?突破創新獎候選案例——準時達國際供應鏈管理有限公司
861 閱讀仿生學:蜂巢帶給供應鏈管理的啟示
836 閱讀人民日報“晚安短信計劃”關注電商西進:拼多多新農人傳遞溫暖
877 閱讀